
- COMPREHENSIVE META ANALYSIS VERSION 3 SERAIL SERIAL
- COMPREHENSIVE META ANALYSIS VERSION 3 SERAIL SOFTWARE
Įxisting evidence showed that most of the COVID-19 cases are missed by screening due to they are unaware they were exposed, and not developed symptoms yet. Effective treatment to block the spread of COVID-19 is not developed yet, hence countries implement non-treatment intervention such as social distancing, isolation, face mask and quarantine to reduce its rapid transmission. Rapid spread of COVID-19 causes an enormous impact on social, economic and health care system in the world. Globally, from the outbreak of the virus up to August 5, 2020, 18 million total confirmed cases and 700, 000 deaths were reported. The 2019 Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) continues to be one of the potential clinical and public health issues in the global population.
COMPREHENSIVE META ANALYSIS VERSION 3 SERAIL SERIAL
In this study, the average serial interval of COVID-19 is shorter than the average incubation period, which suggests that substantial numbers of COVID-19 cases will be attributed to presymptomatic transmission. This systematic review and meta-analysis showed that the weighted pooled mean serial interval and incubation period of COVID-19 were 5.2, and 6.5 days, respectively. Accordingly, the weighted pooled mean incubation period of COVID-19 was 6.5 (95%CI: 5.9–7.1) days. The mean incubation period of COVID-19 also ranged from 4.8 to 9 days. Additionally, to pool the mean incubation period of COVID-19, we included 14 articles. Our meta-analysis showed that the weighted pooled mean serial interval of COVID-19 was 5.2 (95%CI: 4.9–5.5) days. The mean serial interval of COVID-19 ranged from 4. We combined a total of 23 studies to estimate the overall mean serial interval of COVID-19.
COMPREHENSIVE META ANALYSIS VERSION 3 SERAIL SOFTWARE
Microsoft Excel was used for data extraction and R software was used for analysis. A random effect Meta-analysis was employed to determine the pooled estimate with 95% (CI). The NOS adapted for cross-sectional studies was used to evaluate the quality of studies.
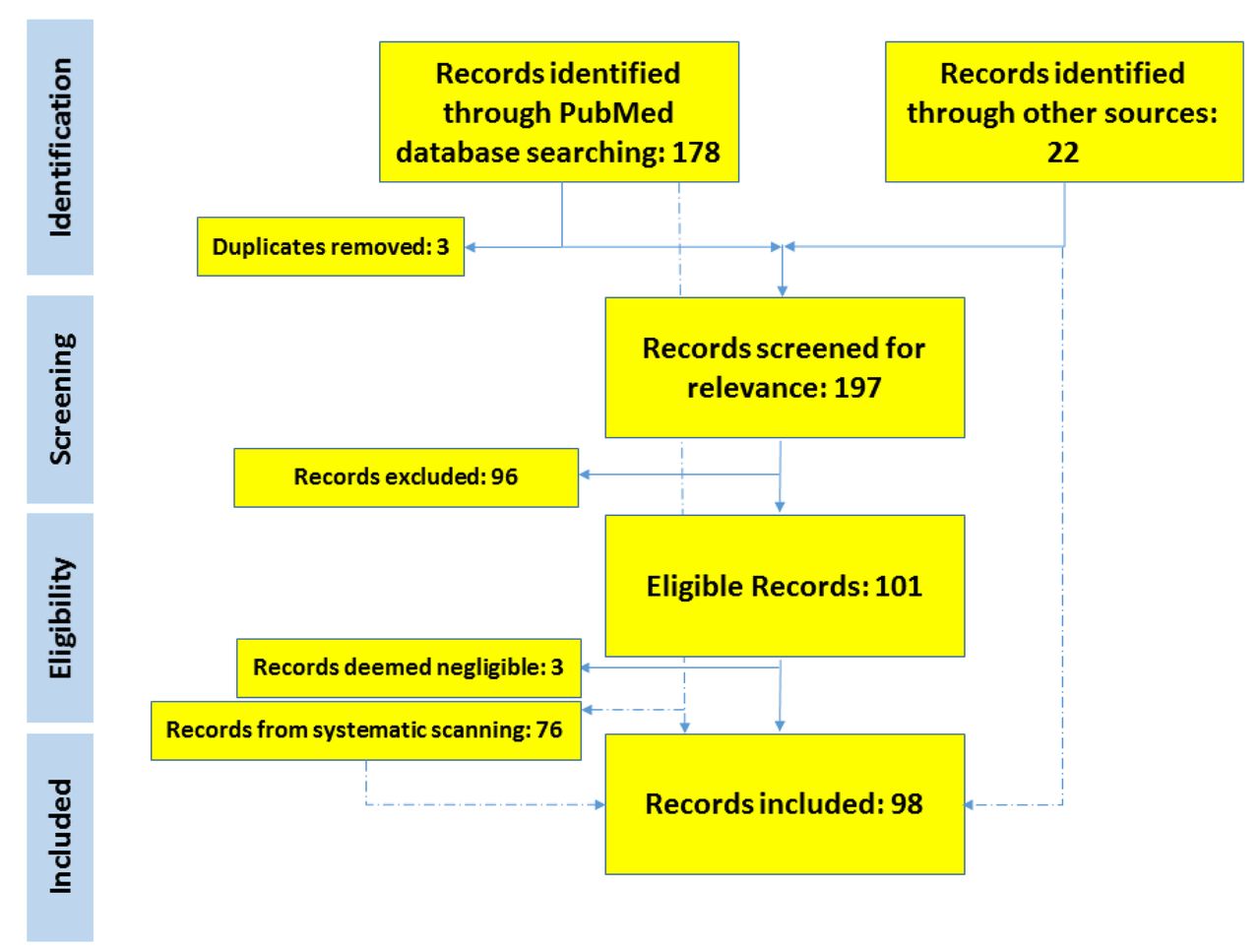
Heterogeneity across studies was assessed using the I 2 and Higgins test. All observational studies either reporting the serial interval or incubation period in persons diagnosed with COVID-19 were included in this study. A comprehensive search strategy was carried out from international electronic databases (Google Scholar, PubMed, Science Direct, Web of Science, CINAHL, and Cochrane Library) by two experienced reviewers (MAA and DBK) authors between the 1st of June and the 31st of July 2020. We followed the PRISMA checklist to present this study. Hence, this study aimed to determine the overall average serial interval and incubation period of COVID-19. Combining findings of existing studies that estimate the average serial interval and incubation period of COVID-19 significantly improves the quality of evidence.

Globally, a number of studies were conducted to estimate the average serial interval and incubation period of COVID-19. Understanding the epidemiological parameters that determine the transmission dynamics of COVID-19 is essential for public health intervention.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
